This post is to help clients decipher the many different options available when purchasing cloud computing with TotalCAE on AWS, either in your AWS account, or hosted by TotalCAE. You can also watch the video instead of reading this post.
Buying on-premises HPC clusters is easy to understand, you can purchase the capacity all upfront, or you can lease the capacity monthly for 3-4 years.
With cloud computing, there are even more flexible options that can make it confusing which option is best for certain types of simulation use cases.
This post will dive into the five major ways to purchase TotalCAE on AWS compute capacity including:
- On-Demand instances.
- Reserved Instances.
- Savings Plans.
- Spot Instances.
- Capacity Blocks
On-Demand Instances

On-Demand instances are true “Pay as You Go” computing. When you need compute capacity, you rent the compute hardware only for the duration of the simulation job, and then the compute hardware is turned off.
Features of On-Demand instances include:
- Power machines on/off based on workload.
- Pay by the hour only for what you use.
- No long-term commitment. True OPEX computing.
The advantages of On-Demand instances for CAE workloads are:
- Good for additional burst overflow capacity to supplement on-premises.
- Good for workloads that you need HPC compute power only occasionally.
- Good as a low-cost disaster recovery (DR) option for on-premises HPC. Cloud can be ready to turn on in a pinch with minimal cost or commitment.
The disadvantages of On-Demand instances for CAE are:
- Renting by the hour is the most expensive way to utilize cloud resources, if you use too much On-Demand the costs add up quickly.
- There is no guarantee that AWS will have the capacity when you need it, so if you need your job to solve immediately, it may have to wait.
- You need to wait for the compute instances to boot up, before your job will start. While this may only take 2-3 minutes for the computer to fully boot, engineers that are not used to waiting for the workload to start may find this annoying.
Is On-Demand Really Infinite?
Many clients are surprised that the cloud does not have infinite capacity. The cloud is at the most basic level just a computer you are renting in some other data center, and even AWS data centers have finite capacity for any particular kind of computer. For this reason, you will occasionally find that you are not able to get On-Demand instances and may need to wait for a period of time for capacity to free up. When this happens you will get an error similar to below:

To work around this, you will need to pick a different instance, different region or data center (Availability Zone), or just wait for free capacity to free up. To prevent this scenario, you can do a Capacity Reservation, or utilize Reserved Instances.
Using On-Demand instances with TotalCAE on AWS
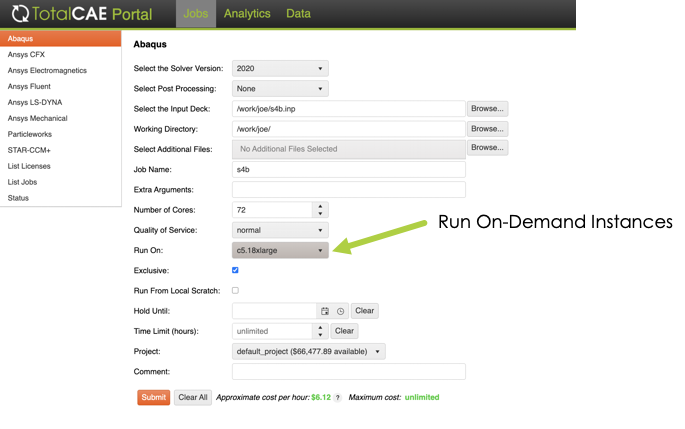
Utilizing On-Demand instances with TotalCAE on AWS is quite simple, just choose from the curated list of machine type to run on, and TotalCAE will automatically take care of powering on the nodes, running your job, and then powering off the nodes.
The screenshot below shows the drop down to select On-Demand instances.
Reserved Instances

Reserved Instances (RI’s) are similar conceptually to buying compute hardware on-premises. You enter a contract to use a certain type machine, operating system, and region for a period of 1 or 3 years. During that period, the machines are left on as you are paying for the machine if you use them, or not. At the end of the period, the machines revert to the On-Demand pricing.
The pros of reserved instances are :
- No waiting for computers to boot up to run your jobs.
- Guaranteed Availability.
- Lowest cost for sustained usage
There are three “payment plans” on how to pay for the fixed contract cost:
- All Upfront: Full payment is made at the start of the term, with no other costs regardless of hours used.
- Partial Upfront: A portion of the cost must be paid upfront and the remaining hours in the term are billed at a discounted hourly rate, you are charged even if the Reserved Instance is not being used.
- No Upfront: You are billed a discounted hourly rate for every hour within the term, even if the Reserved Instance is not being used.
Note in all these options, you have a contractual obligation to pay for the entire term of the reservation, you can’t just stop paying if you change your mind before the end of the term.
The best option is often on how your company wants to handle cashflow and depreciation. ( Note RI’s are lease-like constructs, and are therefore considered CAPEX under recent accounting rules. )
The cons of Reserved Instances are
- You pay if you use the compute or not.
- There is a contractual lock-in of 1 to 3 years, it is CAPEX similar to on-premises.
- They are not as flexible as AWS savings plan due to being locked in to the instance type, operating system, and region ( depending if you choose a convertible RI option).
AWS Savings Plan
AWS savings plans are a newer option similar to Reserved Instances but with much more flexibility in that they allow you to run any instance, in any regions, with any OS in exchange for guaranteeing that you will spend a minimum dollar per hour amount with AWS during the term of 1 or 3 years.
Savings Plans don’t guarantee capacity, but you can combine your savings plan with an On-Demand Capacity Reservation to get the same capacity guarantees as an RI.
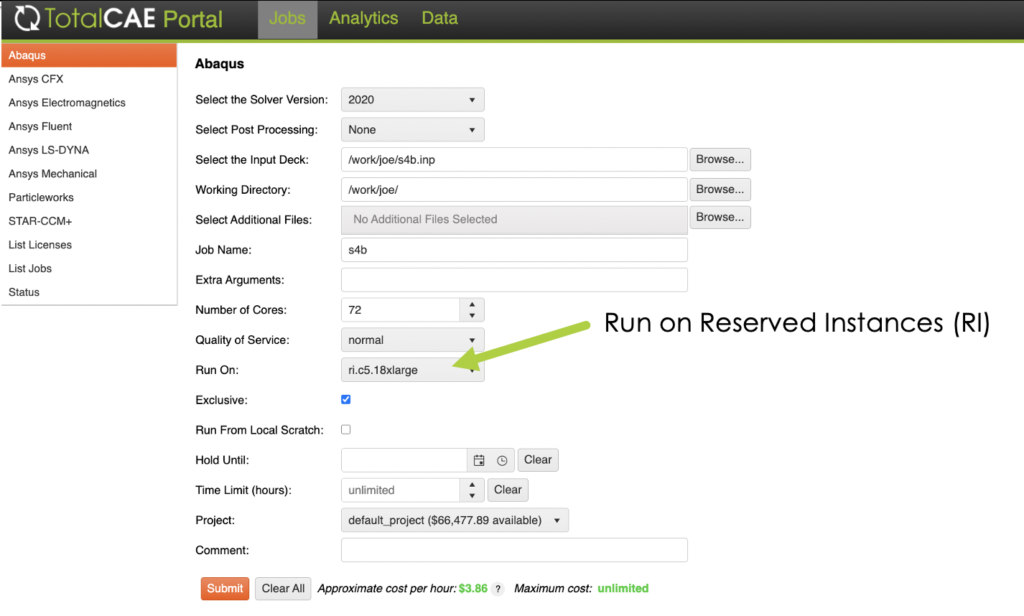
Using Reserved Instances with TotalCAE on AWS
Using Reserved Instances with TotalCAE on AWS is just selecting the reserved instance from the drop down, TotalCAE will immediately run the job on those nodes, which are always powered on and ready to run jobs.
Spot Instances
Spot Instances are the cheapest way to run on the cloud with no commitment, though HPC instances are a better fit for most CAE clients as they are pre-discounted and purpose built for HPC.
Spot Instances are spare compute capacity that are available at up to a 90% discount compared to On-Demand prices. The spot pricing fluctuates and is determined by supply and demand for Amazon EC2 spare capacity. If the Spot capacity is available then your job will run at a significant discount compared to the On Demand rate.
Spot Instances for CAE are best suited when:
- You have non-urgent short running (< 6 hours) workloads.
- You have workloads that can be check pointed in case of being killed by AWS. (Note not all CAE solvers can checkpoint.).
- You are doing Design of Experiments where not every job in the experiment needs to complete to get to the best design.
- Cost is the dominating factor.
One downside to Spot is that there is no guarantee that there is idle capacity to run at a discounted rate to On Demand, so you may have to wait a while for your job to start running.
One caveat of using Spot instances is your job can be interrupted if AWS reclaims those instances, though in practice it occurs less than 5% of the time for instances we use.
Many of our clients prefer not using Spot for longer running jobs as they don’t want their jobs to be killed.
Using Spot Instances with TotalCAE on AWS
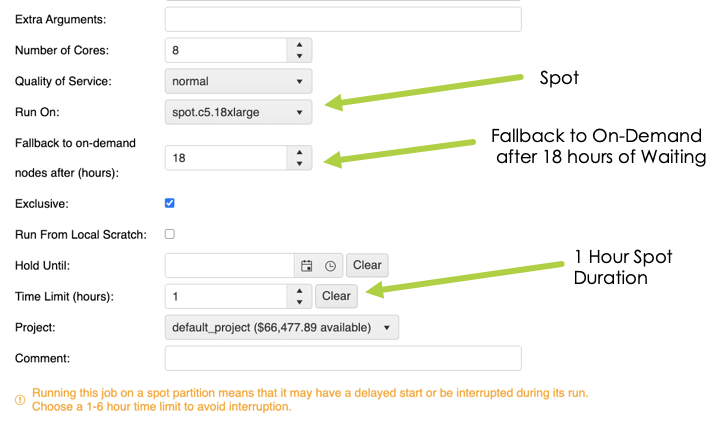
TotalCAE makes it dead simple to use Spot Instances to
- Run at a cheaper cost.
- Fallback to On Demand if cheaper spot pricing is not available in time.
- Not be killed if under 6 hours
Run at Cheaper Cost
If your job is able to run on Spot for the chosen instance, you will automatically capture the savings that were estimated in the TotalCAE portal.
Fallback to On Demand
While savings money is important, engineers ultimately need to get their answer back in time to impact the design. In many cases, engineers are utilizing cloud to run urgent jobs that might have queued on-premises, and getting the answer back cheaply but late is not really not useful.
To avoid this, TotalCAE offers a unique ability for engineers to first try for the lower price with Spot Instances, BUT if AWS does not accept the spot request in time, TotalCAE will fallback the job to On-Demand to ensure your job will start, not be killed, and get you the answer when you need it.
Ensure Short Jobs Are Not Killed
TotalCAE makes it easy to specify that you want to submit a job that runs in less than 6 hours to not be killed. Simply set a Time Limit of up to 6 hours, and we automatically will provision the Spot Block duration so that if AWS accepts your spot request, it will not be killed before the time limit. Note that utilizing this feature reduces the odds that AWS will fill the spot request.
EC2 Capacity Block Reservations
Capacity Block Reservations are used to reserve many popular GPU instance types. You choose the amount of resources you need and duration, and AWS will find the earliest time slot for you to reserve the capacity which you then pre-pay for, and use when your designated time arrives. This is analogous to a pre-paid hotel reservation with a no-cancellation policy. You can read more about this type of scheduled reservation at https://aws.amazon.com/ec2/capacityblocks/
Summary
AWS offers many different flexible pricing options for running compute workloads, and TotalCAE makes it very simple to adopt and mix and match all of these options. Below is a summary table on the different plans discussed in this section. If you are interested in learning more, please contact info at totalcae dot com.
| Instance Type | Comment | Minimum Term to Pay | Upgradeable Hardware | Savings Over Base On-Demand | CapEx or OpEx |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| On-Demand Instances | Pay As You Go | N/A | Yes | Base | OpEx |
| Reserved Instances | Prepay With Optional Upgrade Option | 1-3 years | Yes | 31%-60% | CapEx |
| Savings Plan | Spend a Fixed Dollar Amount Per Hour | 1-3 years | Yes | Up to 66% | CapEx |
| Spot Instances | Reduced Price For Unused Capacity | N/A | Yes | 30-90% | OpEx |
If you are interested in a deep dive into these options download our free TotalCAE on AWS e-book here.
